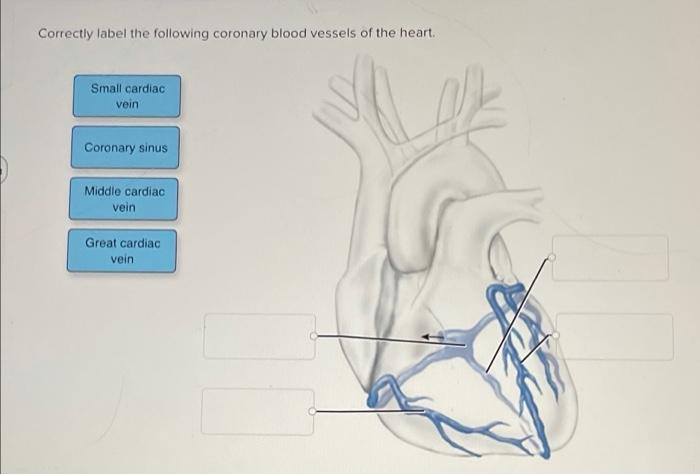
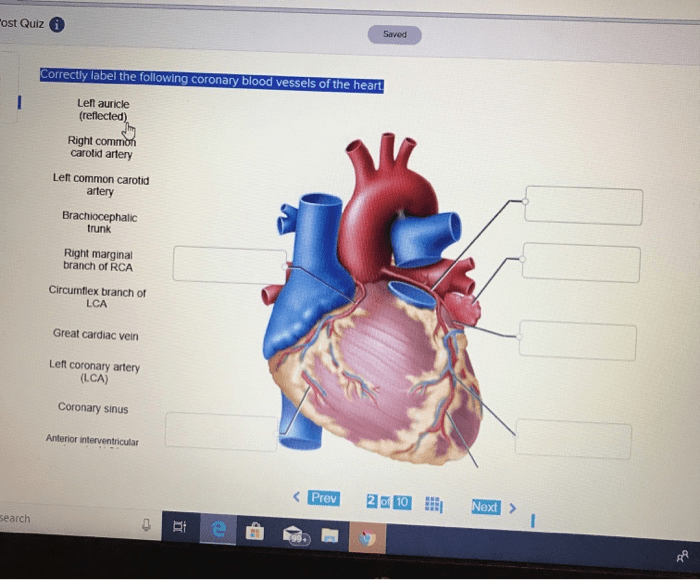
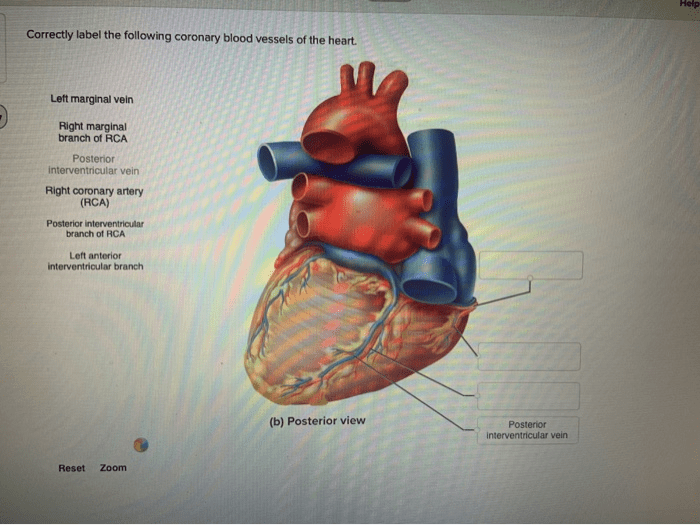
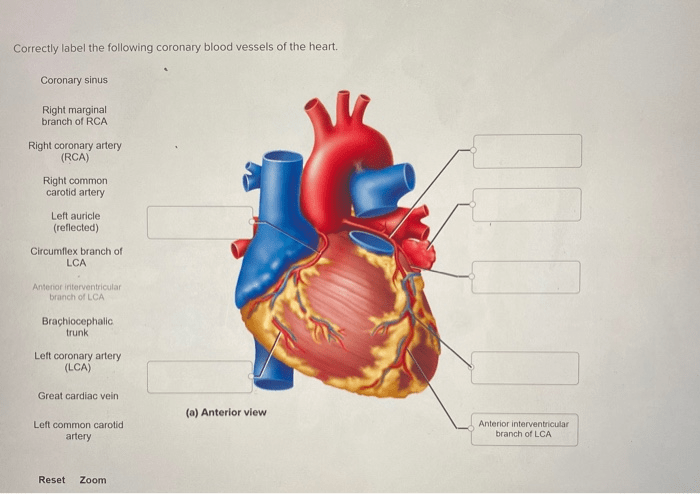
Correctly label the following coronary blood vessels of the heart. – Correctly labeling the coronary blood vessels of the heart is of paramount importance in various medical procedures. This comprehensive guide delves into the anatomical location, function, and clinical significance of these vessels, providing healthcare professionals with a thorough understanding of their crucial role in maintaining cardiac health.
The coronary arteries, including the left main coronary artery, left anterior descending artery, and right coronary artery, supply oxygenated blood to the heart muscle. The coronary veins, such as the great cardiac vein, middle cardiac vein, and small cardiac vein, drain deoxygenated blood from the heart.
Understanding the drainage pattern of these veins is essential for diagnosing and treating cardiac conditions.
Coronary Blood Vessels of the Heart: Overview
Coronary blood vessels are a network of arteries and veins that supply blood to the heart muscle. They are located on the surface of the heart and are responsible for delivering oxygen and nutrients to the myocardium, the muscular layer of the heart.
The coronary blood vessels play a crucial role in maintaining heart health and function.
Major Coronary Arteries
- Left Main Coronary Artery:Originates from the aorta and gives rise to the left anterior descending (LAD) and left circumflex (LCX) arteries.
- Left Anterior Descending (LAD) Artery:Supplies blood to the anterior and lateral walls of the left ventricle.
- Left Circumflex (LCX) Artery:Supplies blood to the posterior wall of the left ventricle and the atrioventricular node.
- Right Coronary Artery (RCA):Originates from the aorta and supplies blood to the right atrium, right ventricle, and inferior wall of the left ventricle.
Coronary Veins: Correctly Label The Following Coronary Blood Vessels Of The Heart.
- Great Cardiac Vein:Drains blood from the anterior and lateral walls of the left ventricle.
- Middle Cardiac Vein:Drains blood from the posterior wall of the left ventricle.
- Small Cardiac Vein:Drains blood from the right atrium and ventricle.
- Coronary Sinus:Collects blood from all the coronary veins and empties into the right atrium.
Collateral Circulation
Collateral circulation refers to the development of new blood vessels that bypass obstructed coronary arteries. This occurs in response to coronary artery disease, where atherosclerotic plaques narrow or block the arteries, reducing blood flow to the heart. Collateral circulation helps maintain blood supply to the heart muscle, preventing ischemia and infarction.
Clinical Significance
Correctly labeling coronary blood vessels is crucial for medical procedures such as coronary angiography and stenting. Mislabeling can lead to incorrect diagnosis and inappropriate treatment, potentially compromising patient safety. Various techniques, including fluoroscopy, intravascular ultrasound, and optical coherence tomography, are used to accurately identify and label coronary blood vessels.
User Queries
What are the three major coronary arteries?
The three major coronary arteries are the left main coronary artery, left anterior descending artery, and right coronary artery.
What is the function of the coronary veins?
The coronary veins drain deoxygenated blood from the heart muscle.
Why is it important to correctly label the coronary blood vessels?
Correctly labeling the coronary blood vessels is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment of cardiac conditions.