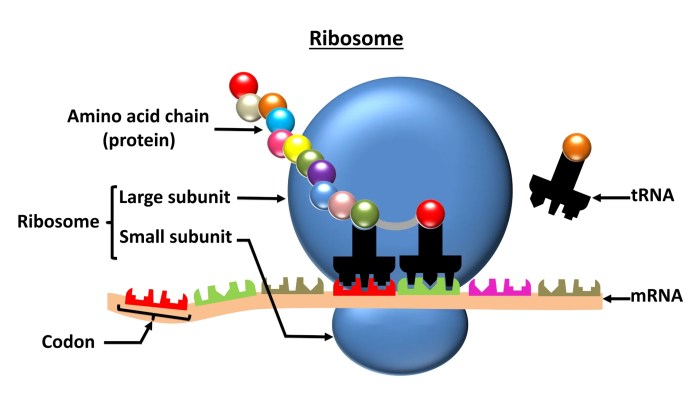
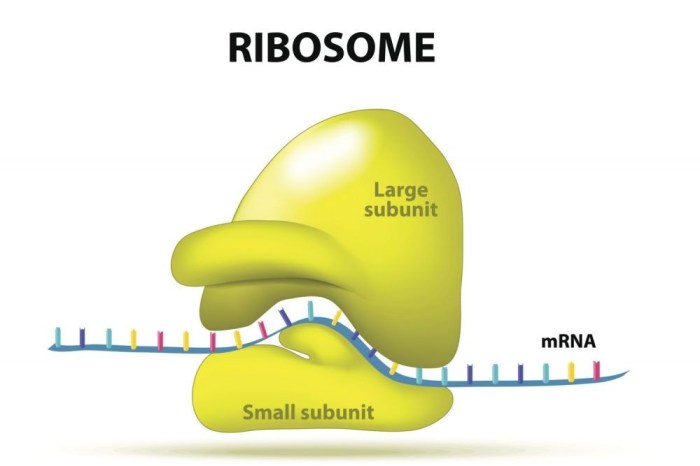
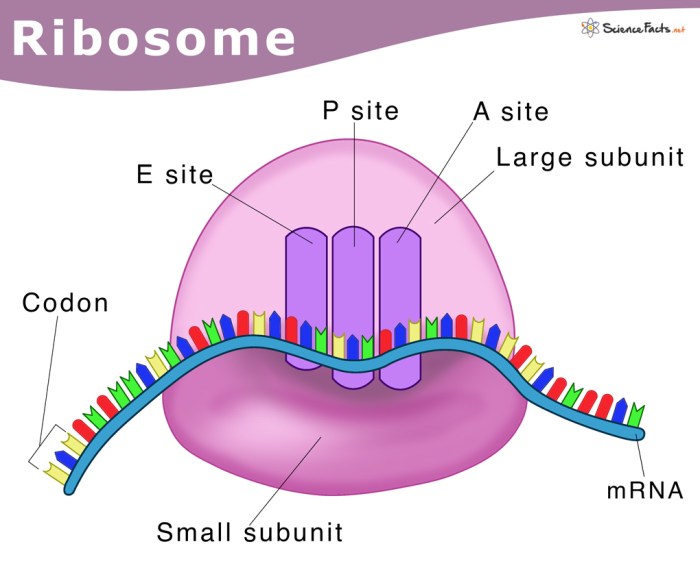
Small bumps located on portions of the endoplasmic reticulum, known as ribosomes, play a crucial role in protein synthesis and other cellular processes. These bumps are composed of RNA and protein and are responsible for translating the genetic code into functional proteins.
This article explores the structure, function, regulation, and clinical significance of these small bumps on the endoplasmic reticulum.
Structure of the Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): Small Bumps Located On Portions Of The Endoplasmic Reticulum
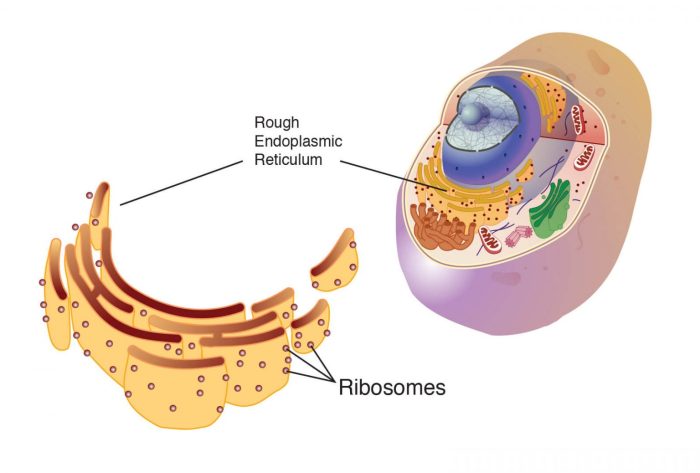
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a complex organelle found in eukaryotic cells. It is a continuous membrane system that forms a network of flattened sacs and tubules throughout the cytoplasm. The ER is divided into two main types:
- Rough ER:Covered with ribosomes, giving it a rough appearance under the microscope. Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis.
- Smooth ER:Lacks ribosomes and is involved in various cellular processes, including lipid metabolism, detoxification, and calcium storage.
Detailed Illustration of the ER:[Berikan ilustrasi yang menunjukkan komponen ER, termasuk membran, ribosom, lumen, dan vesikel.]
Small Bumps on the ER
Small bumps are observed on the surface of the rough ER in electron micrographs. These bumps vary in size and shape, but they are typically spherical or elliptical. They are often referred to as “ribosomes” or “polyribosomes.” Different Types of Small Bumps:
- Monosomes:Single ribosomes attached to the ER membrane.
- Polysomes:Multiple ribosomes attached to the same mRNA molecule, forming a chain.
Composition and Function of Small Bumps, Small bumps located on portions of the endoplasmic reticulum
Small bumps on the ER are composed of ribosomes, which are complex molecular machines responsible for protein synthesis. Ribosomes consist of two subunits, a large subunit and a small subunit, which assemble on the mRNA molecule to translate the genetic code into a chain of amino acids.
Role of Small Bumps in Protein Synthesis:
- Ribosomes bind to the mRNA and read the sequence of codons.
- Each codon specifies a specific amino acid.
- Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules bring the correct amino acids to the ribosome.
- Ribosomes catalyze the formation of peptide bonds between the amino acids, creating a growing polypeptide chain.
Regulation of Small Bumps
The formation and distribution of small bumps on the ER are regulated by several factors:
- mRNA availability:The presence of mRNA molecules triggers the assembly of ribosomes on the ER membrane.
- Protein synthesis rate:Increased protein synthesis leads to an increase in the number of ribosomes attached to the ER.
- Signal transduction pathways:Cellular signaling molecules can influence the distribution and activity of ribosomes on the ER.
Relationship to Cellular Function
Small bumps on the ER are essential for protein synthesis, which is crucial for the cell’s function. Proteins are involved in a wide range of cellular processes, including:
- Enzymes:Catalyze chemical reactions.
- Structural proteins:Provide support and shape to the cell.
- Hormones:Regulate various bodily functions.
Implications of Abnormalities:Defects in the formation or function of small bumps can lead to disruptions in protein synthesis, resulting in various cellular dysfunctions and diseases.
Methods for Studying Small Bumps
Various experimental techniques are used to study small bumps on the ER:
- Electron microscopy:Allows visualization of the ER and ribosomes at high resolution.
- Immunolabeling:Antibodies specific to ribosomes can be used to label and identify ribosomes on the ER.
- Ribosome profiling:A technique that combines ribosome footprinting with RNA sequencing to study the distribution of ribosomes on mRNA molecules.
Advantages and Limitations:Each technique has its advantages and limitations, providing complementary information about small bumps on the ER.
Clinical Significance
Small bumps on the ER have clinical significance in several ways:
- Diseases:Abnormalities in ribosome function can contribute to various diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and metabolic syndromes.
- Therapeutic applications:Targeting ribosomes and protein synthesis is a potential strategy for treating diseases.
Examples:
- Cancer:Ribosome biogenesis and function are often dysregulated in cancer cells, making them potential targets for cancer therapy.
- Neurodegenerative disorders:Defects in protein synthesis have been implicated in the development of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease.
Future Research Directions
Future research on small bumps on the ER will focus on:
- Understanding the mechanisms regulating ribosome assembly and function.
- Investigating the role of ribosomes in cellular signaling and disease pathogenesis.
- Developing novel therapeutic strategies targeting ribosomes and protein synthesis.
FAQ Insights
What are small bumps on the endoplasmic reticulum?
Small bumps on the endoplasmic reticulum are ribosomes, which are cellular structures responsible for protein synthesis.
What is the function of ribosomes?
Ribosomes translate the genetic code into functional proteins, which are essential for various cellular processes.
What is the clinical significance of small bumps on the endoplasmic reticulum?
Abnormalities in the formation or function of ribosomes can lead to various diseases, including certain types of cancer and neurodegenerative disorders.