Introducing the protein synthesis and amino acid worksheet answer key, a comprehensive guide to unraveling the intricacies of protein synthesis. This document serves as an authoritative resource for students and professionals alike, providing a deep dive into the fundamental processes and components involved in protein production.
Delving into the realm of protein synthesis, we will explore the critical roles of DNA, RNA, and ribosomes, deciphering the intricate mechanisms that govern the translation of genetic information into functional proteins. Additionally, we will delve into the diverse world of amino acids, examining their chemical properties and their significance as the building blocks of proteins.
Protein Synthesis Overview
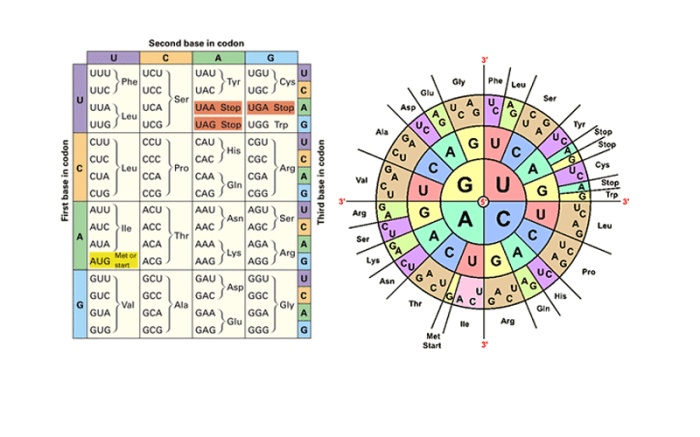
Protein synthesis is the process by which cells create proteins, which are essential molecules for life. It involves the decoding of genetic information from DNA into a sequence of amino acids, which are then assembled into proteins.
DNA, RNA, and ribosomes are key players in protein synthesis. DNA contains the genetic code for proteins, while RNA carries the code from DNA to the ribosomes. Ribosomes are the cellular structures where protein synthesis takes place.
Amino Acids and Their Role
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. There are 20 common amino acids, each with a unique structure and chemical properties.
- Alanine (Ala)
- Arginine (Arg)
- Asparagine (Asn)
- Aspartic acid (Asp)
- Cysteine (Cys)
- Glutamic acid (Glu)
- Glutamine (Gln)
- Glycine (Gly)
- Histidine (His)
- Isoleucine (Ile)
- Leucine (Leu)
- Lysine (Lys)
- Methionine (Met)
- Phenylalanine (Phe)
- Proline (Pro)
- Serine (Ser)
- Threonine (Thr)
- Tryptophan (Trp)
- Tyrosine (Tyr)
- Valine (Val)
Amino acids are classified based on their side chain properties, such as polarity, charge, and size.
Transcription and Translation
Transcription
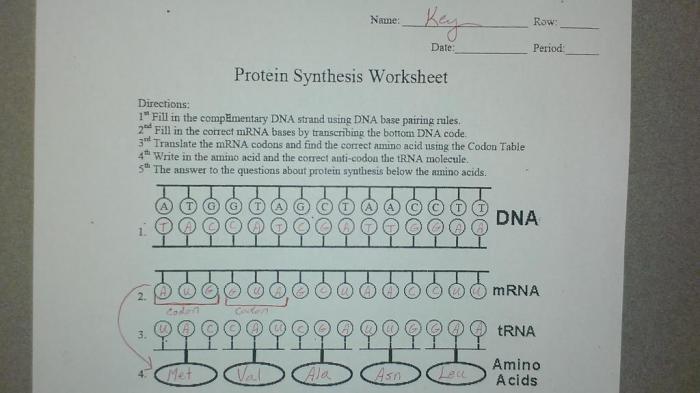
Transcription is the process of copying the genetic code from DNA into messenger RNA (mRNA).
During transcription, an enzyme called RNA polymerase binds to the DNA template and synthesizes a complementary mRNA molecule.
Translation
Translation is the process of decoding the mRNA code into a sequence of amino acids.
Translation occurs on ribosomes. Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules carry amino acids to the ribosome, where they are added to the growing polypeptide chain based on the mRNA code.
Genetic Code
The genetic code is a set of rules that determines how the sequence of nucleotides in mRNA is translated into the sequence of amino acids in proteins.
Each amino acid is encoded by a specific codon, which is a sequence of three nucleotides.
Post-Translational Modifications: Protein Synthesis And Amino Acid Worksheet Answer Key

Post-translational modifications are chemical changes that occur to proteins after they have been synthesized.
These modifications can affect the protein’s structure, function, and stability.
- Phosphorylation
- Glycosylation
- Ubiquitination
- Acetylation
- Methylation
Post-translational modifications are essential for regulating protein function and cellular processes.
Protein Structure and Function
Proteins have four levels of structure: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary.
Primary Structure
The primary structure of a protein is its amino acid sequence.
Secondary Structure
The secondary structure of a protein is formed by hydrogen bonds between the amino acids in the polypeptide chain.
Common secondary structures include alpha-helices and beta-sheets.
Tertiary Structure
The tertiary structure of a protein is formed by interactions between the side chains of the amino acids.
These interactions can include hydrophobic interactions, hydrogen bonds, and disulfide bonds.
Quaternary Structure, Protein synthesis and amino acid worksheet answer key
The quaternary structure of a protein is formed by the interactions between multiple polypeptide chains.
Quaternary structure is found in proteins that are composed of multiple subunits.
Protein Synthesis Disorders
Protein synthesis disorders are genetic conditions that affect the synthesis of proteins.
These disorders can result in a variety of symptoms, depending on the specific protein that is affected.
- Sickle cell anemia
- Cystic fibrosis
- Tay-Sachs disease
- Phenylketonuria
- Albinism
Protein synthesis disorders can be treated with a variety of methods, depending on the specific disorder.
Clarifying Questions
What is the significance of protein synthesis in biological processes?
Protein synthesis is essential for virtually all cellular functions, including growth, repair, and metabolism. Proteins act as enzymes, hormones, structural components, and signaling molecules, playing crucial roles in maintaining homeostasis and orchestrating cellular processes.
How does the genetic code determine the sequence of amino acids in proteins?
The genetic code is a set of rules that governs the translation of mRNA into a specific sequence of amino acids. Each codon, a sequence of three nucleotides, corresponds to a specific amino acid or a stop signal. This code ensures the precise assembly of amino acids in the correct order, as specified by the DNA sequence.
What are the common types of post-translational modifications?
Post-translational modifications are chemical changes that occur to proteins after they have been synthesized. These modifications include phosphorylation, glycosylation, ubiquitination, and acetylation. They can alter protein stability, activity, localization, and interactions, thereby regulating protein function and cellular processes.