The evidence of evolution worksheet answer key embarks on an extraordinary journey through the annals of scientific discovery, unveiling the irrefutable evidence that underpins the theory of evolution. This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse realms of paleontology, comparative anatomy, molecular biology, biogeography, developmental biology, and artificial selection, providing a panoramic view of the evolutionary forces that have shaped life on Earth.
From the fossilized remains of ancient creatures to the intricate genetic similarities among living organisms, this worksheet unveils the compelling evidence that supports the concept of common ancestry and the gradual transformation of species over time. Prepare to embark on an enlightening exploration of the scientific foundations of evolution, unlocking the secrets of our evolutionary heritage.
Fossil Record
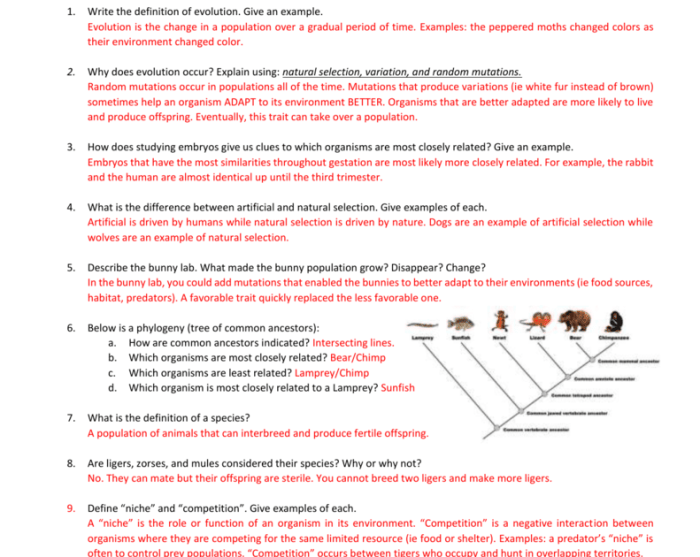
Fossils provide direct evidence of past life and the changes that have occurred over time. They show that organisms have evolved from simpler forms to more complex ones, and that species that once existed are now extinct.
Transitional Fossils, Evidence of evolution worksheet answer key
- Fossils that show characteristics of two different groups, providing evidence of evolutionary transitions.
- Examples: Archaeopteryx(bird-like reptile), Tiktaalik(fish-like amphibian).
Significance of the Fossil Record
- Provides a chronological record of the history of life on Earth.
- Helps determine the age of rock layers and the relative timing of evolutionary events.
- Reveals the extinction and origination of species, providing insights into environmental changes and mass extinction events.
Comparative Anatomy
Comparing the anatomical structures of different organisms reveals similarities and differences that indicate evolutionary relationships.
Homologous Structures
- Structures that have the same basic form and developmental origin, but may serve different functions.
- Examples: Forelimbs of humans, bats, and whales.
Analogous Structures
- Structures that serve similar functions but have different origins and forms.
- Examples: Wings of birds and insects.
Vestigial Structures
- Structures that have no apparent function in an organism but are homologous to functional structures in related species.
- Examples: Hind leg bones in whales, tailbone in humans.
Molecular Biology
DNA and protein sequences provide powerful evidence of evolutionary relationships.
Genetic Mutations and Genetic Drift
- Mutations are changes in DNA sequences that introduce genetic variation.
- Genetic drift is the random change in gene frequencies within a population.
- Together, these processes contribute to genetic diversity and the evolution of new traits.
Molecular Evidence for Common Ancestry
- Similarities in DNA and protein sequences across different species indicate shared ancestry.
- Molecular clocks can be used to estimate the time since species diverged.
- Genetic evidence supports the theory of universal common descent.
Biogeography: Evidence Of Evolution Worksheet Answer Key
The distribution of species across different geographic regions provides insights into evolutionary processes.
Plate Tectonics and Dispersal
- Plate tectonics has played a major role in shaping biogeographic patterns.
- Dispersal events, such as the migration of species across land bridges, can also influence species distribution.
Endemic Species
- Species that are found only in a specific geographic region.
- Endemic species provide evidence of evolutionary isolation and speciation.
Developmental Biology
Embryological development provides insights into evolutionary relationships and the conservation of developmental genes.
Recapitulation Theory
- Theory that embryonic development recapitulates the evolutionary history of the species.
- While there are some similarities in early developmental stages, recapitulation is not strictly accurate.
Developmental Similarities and Differences
- Similarities in embryonic development suggest shared ancestry.
- Differences in development reflect adaptations to different environments and lifestyles.
Artificial Selection
Artificial selection, practiced by humans, provides a controlled example of evolution.
Selective Breeding
- Humans breed organisms to enhance desirable traits.
- This has led to the development of new breeds and varieties of plants and animals.
Examples of Artificial Selection
- Agriculture: Selective breeding of crops for increased yield and disease resistance.
- Animal husbandry: Selective breeding of livestock for desirable traits, such as increased meat production.
- Pet breeding: Selective breeding of companion animals for specific characteristics, such as appearance or behavior.
User Queries
What is the fossil record, and how does it provide evidence of evolution?
The fossil record is a chronological record of past life preserved in the Earth’s geological formations. It provides evidence of evolution by documenting the gradual changes in the morphology and diversity of organisms over time, showcasing the transition from simpler to more complex forms.
How does comparative anatomy support the theory of evolution?
Comparative anatomy examines the similarities and differences in anatomical structures across different species. It reveals homologous structures, shared by different species due to common ancestry, and analogous structures, which serve similar functions but have evolved independently. Vestigial structures, remnants of ancestral structures that no longer serve an apparent function, also provide evidence of evolutionary relationships.
What role does molecular biology play in understanding evolution?
Molecular biology analyzes DNA and protein sequences to uncover genetic similarities and differences among species. Genetic mutations and genetic drift contribute to genetic diversity, providing the raw material for natural selection to act upon. Comparative genomics reveals shared genetic sequences, indicating common ancestry and evolutionary relatedness.


